After spending a year and a half researching the dairy industry for our documentary series Milk and Money, Re: journalist Baz Macdonald decided to put his money where his mouth is and work as a dairy farmer for a week. He shares the insight it gave.
Milk and Money is a six-part documentary series by Re: investigating New Zealand’s dairy industry. You can watch it now on Re: and TVNZ OnDemand.
Content warning: This article contains images of stillborn calves.
There are some things you can only learn from experiencing them firsthand. And despite growing up in and around farms in Southland and spending my summers working at the local freezing works, I had never worked on a dairy farm.
I knew that if I really wanted to understand the dairy industry, I would need to get my hands dirty - likely with shit.
So I reached out to Sam Hogg, a young dairy farmer I had met producing the documentary, to ask if I could work on his family’s organic dairy farm, Mingiroa Farms, about 25 minutes north of Palmerston North in Manawatu.
Here’s what I learnt.
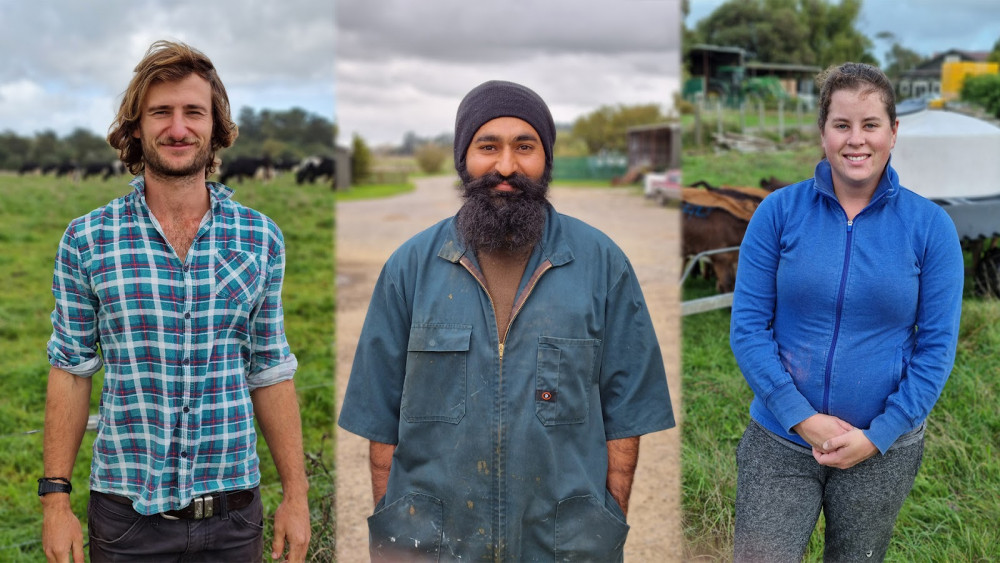

The Mingiroa Farm team. Left: Sam Hogg - owner/operator/all around good guy. Middle: Sukh - dairy manager/family man. Right: Sammy - dairy assistant/calf whisperer
The job is friggin hard: physically and emotionally
It’s a cliche, but a dairy farmer really does do more before breakfast than most people do in a day.
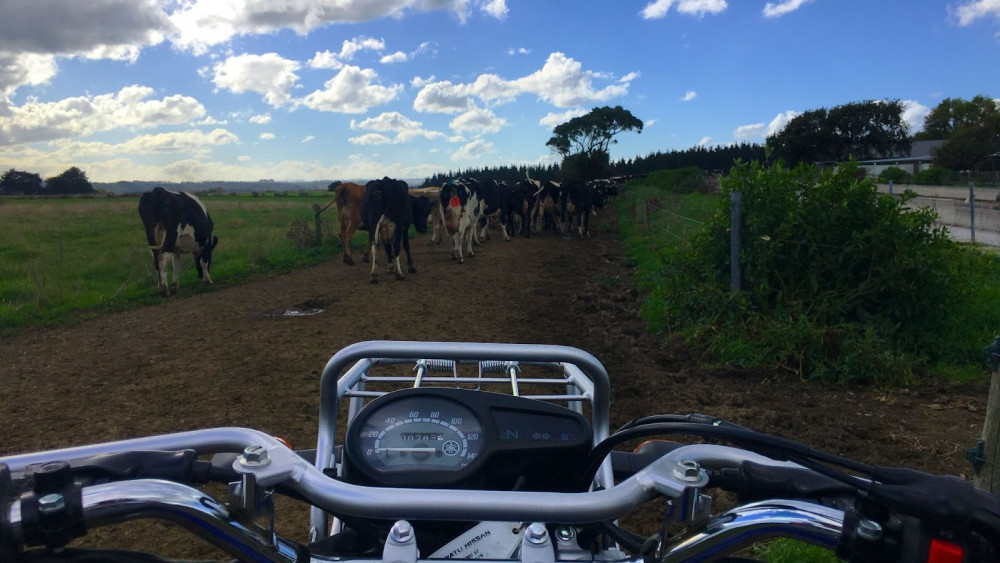

My view from the motorbike corralling the girls
Most days I worked from 5:30am to 5pm.
People shudder at the idea of starting work at 5:30am, but the early mornings ended up being my favourite time. It was liberating to start your day by jumping straight on a motorbike and rocketing across a paddock. The crispness of the air whipping your face, the sun breaking the horizon, the mild-mannered greeting of the cows.
But from there, my days were jammed with a routine of milking, maintaining the land, and looking after the cows that left me physically exhausted at the end of every day.
Me milking after five days of practice - still pretty clumsy, but not bad for only a week I reckon
The job was also quite emotionally intense, especially because I was there during calving season. In the week I was there, there were two stillborn calves.
Even though Sam had dealt with this before - these were the third and forth stillbirths of 70 calves born that season - it was clear how difficult losing a calf was to Sam.
“You spend all that time selecting their parents, looking after their mothers,” he told me. “You have chosen them to be in the herd, to be a part of your life.”
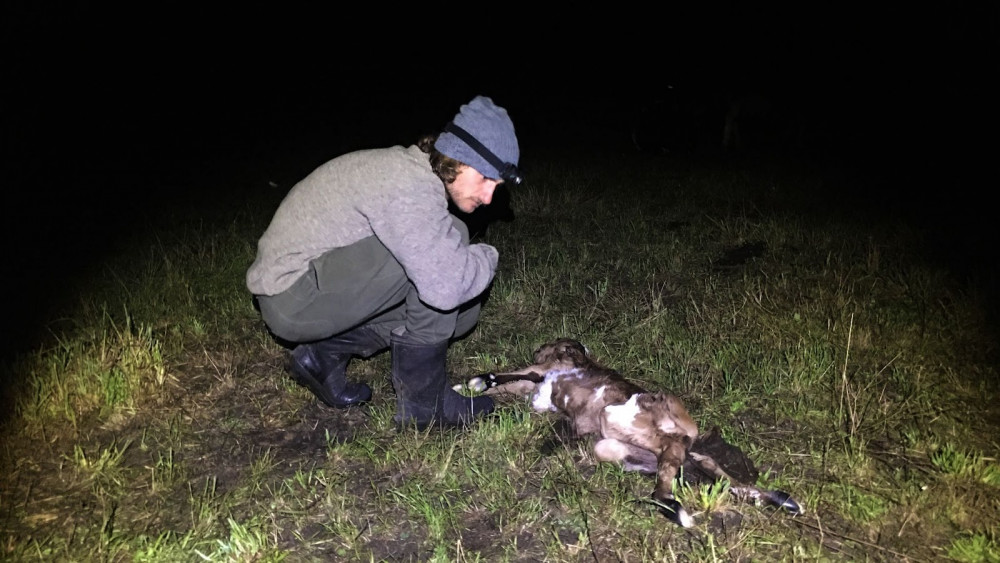

Sam inspecting the stillborn calf
Mental health is a big issue in the dairy industry. A recent DairyNZ report found 62 percent of dairy farmers said they, or someone on their farm, had experienced mental health issues in the past 12 months.
A week was too short for me to experience any long-term impact on my mental health, but I could see how the work could take a toll - especially if you lived on the farm and didn’t get to mentally separate from it at the end of your work day.
You’re really as much a nurse as you are a farmer
Milking on Sam’s farm was as much about evaluating the health of the cows as taking their milk. As each cow goes past, the milkers quickly evaluate the wellness of each cow and make efficient decisions about what kind of medicine they need, applying it, and deciding whether they need further assessment.
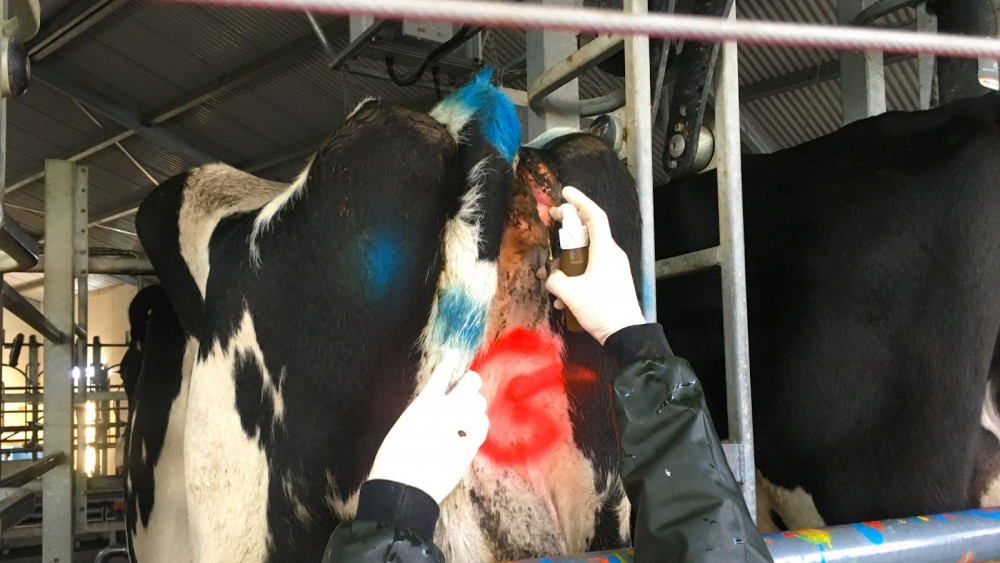
The most efficient way to give the cows medicine in the milking shed is to apply it straight to their vulva
This focus on health was particularly true on Sam’s organic farm, where many conventional medicines and antibiotics are not allowed. This means that illness prevention is their best defense, and so extra attention is paid to the health of each animal, and homeopathic sprays are applied as a preventative measure.
The most common malady the farmers had to deal with is mastitis, or a breast infection. The process of constantly milking cows means this is quite common, with approximately a quarter of all dairy cows in New Zealand having mastitis during milking season.
Cows with mastitis are milked separately to the other cows so that their milk doesn’t get sent to consumers. Which is good, because their milk can be gnarly, coming out in congealed lumps of pus and milk.
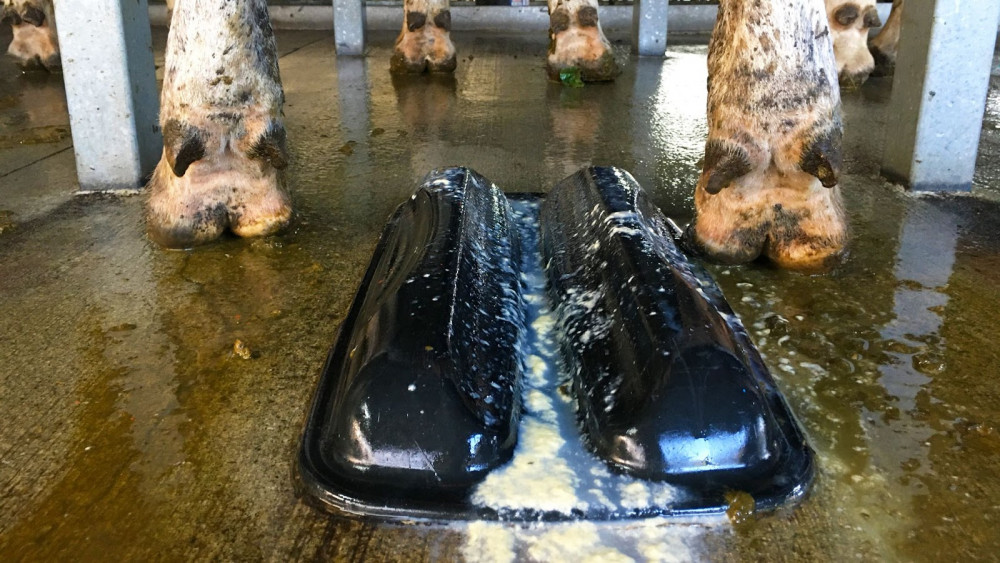

The first pull of milk from a cow with mastitis was lumpy like this, and occasionally would be tinged red with blood
The cows have distinct personalities and social groups
In only a week I began to recognise individual cows and their personalities from within the herd of 300.
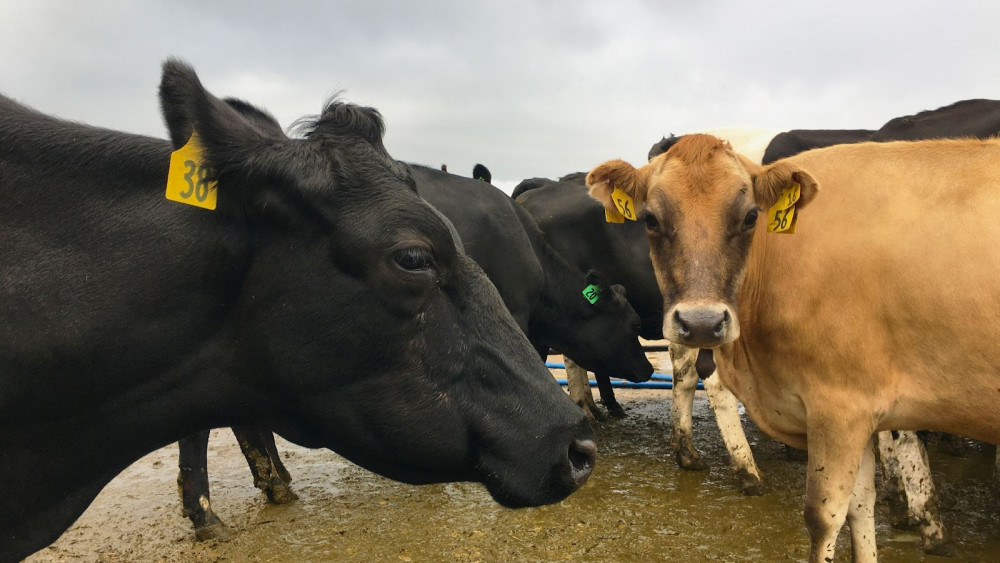

Sylvia (#38), in her own world as usual
The cows with the strongest personalities often end up getting names. Among my favourites were Lola, a sweet old cow who bloody loved a scratch, and Sylvia, a cheeky girl who always did whatever she pleased no matter how much I asked otherwise.
I began to recognise social groups within the herd as well. There were always certain cows you could expect to find together, and whenever the herd walked past cows in a different paddock there was always a small group who would lag behind to interact with them over the fence.
Giving Lola a scratch before milking
Dairy cows are shitting machines
There were times where it felt like I was farming shit, not cows.
Cows shit A LOT! Each cow produces about 70kg of waste every day. That is more than the weight of your average person. So essentially, a cow produces a person’s worth of piss and shit every day.
This makes getting them together in one place for milking a messy affair. They create literal streams of piss and shit in the holding yard that had to be cleaned up (generally by yours truly).
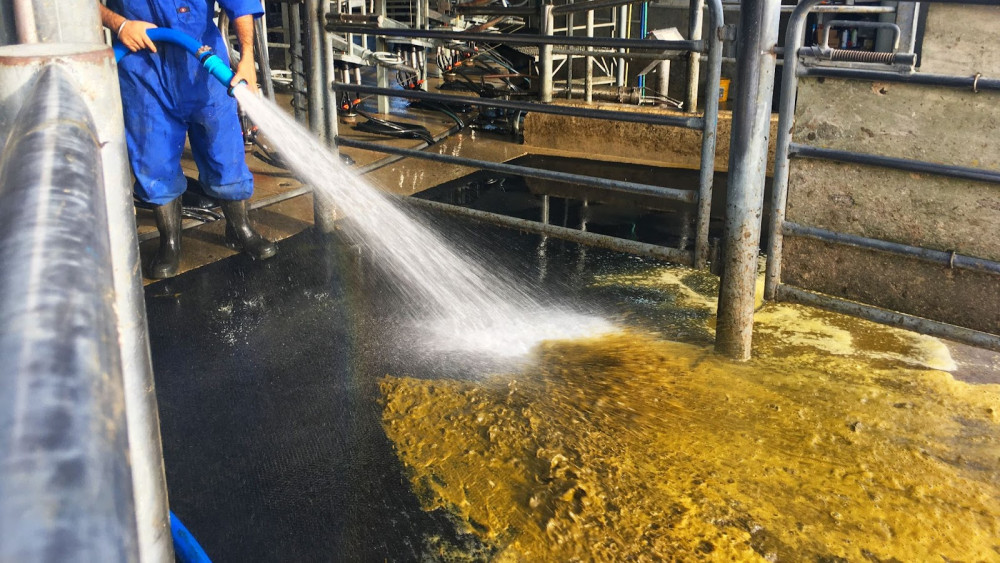

Sukh spraying down the holding yard after milking
I did the math, and I estimate I got poo on my face 68 times across the week.
Milking cows have constant diarrhea because of the intense strain their metabolism is under from producing that much milk.
After years of seeing dairy cows’ poo as a stream of liquid crap, I had forgotten that this isn’t necessarily a natural state. A good reminder of that was visiting the cows waiting to give birth who were not yet actively milking, and seeing their milking break had resulted in normal looking firm cow pats.
The holding yard during milking
The process can feel unnatural
There were moments I experienced deep pangs of discomfort at the process of dairy farming. Not because the poo was gross (though it often could be), but because when I thought about the rates of mastitis, or the constant diarrhea, I was confronted by how unnatural the way we milk our cows is.
In most forms of pasture-based farming, animals get to live their life in a generally natural way because all we need them to do is grow. A beef cow’s whole job is to eat grass, and grow big. Unnatural processes only happen once a year or once a lifetime, like slaughter of a full-grown animal at a factory, or shearing a sheep once a season.
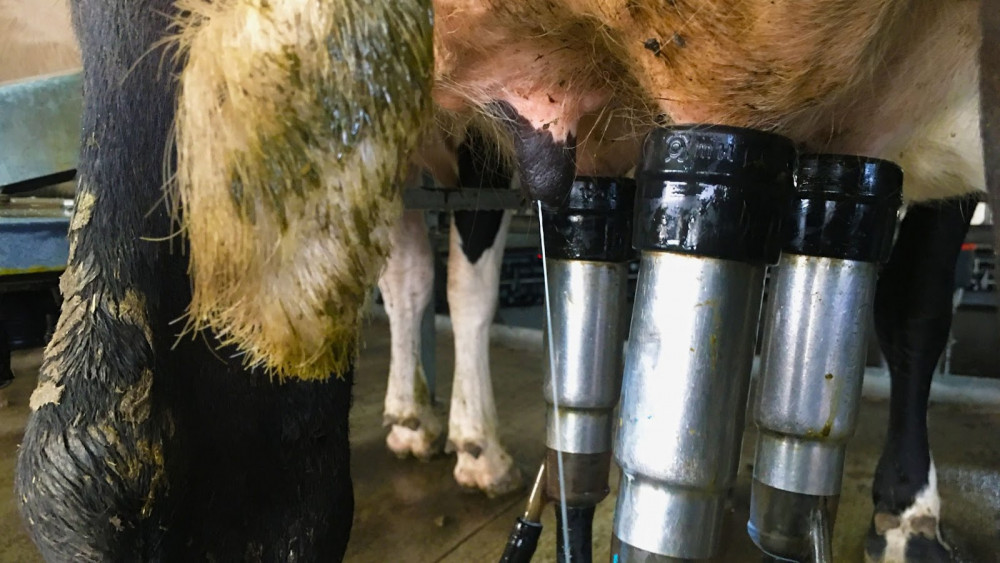

A freely milking teat, with suctions cups on the rest
However, on a dairy farm this unnatural clash happens every day.
From the first time they give birth, cows are initiated in a twice-daily cycle of walking to a shed and onto a rotating mechanical wheel where a machine pumps milk from them.
They spend most of their lives pregnant to stay part of that cycle. Until the year they either stop producing milk (usually because they don’t get pregnant, or aren’t producing enough), then they get sent to the slaughterhouse.
I’m not saying that my week dairy farming made me conclude that dairy farming is innately wrong - though of course there are people who think it is - but there were definitely moments that made me go, “this is a bit strange when you think about it”.
Cows on the rotary machine, and their milk being diverted to feed the calves
Calves are a joy - I’m so glad I didn’t have to kill them
Of course, impregnating cows once a year so they keep producing milk also makes a lot of calves.
My week on the farm occured right at the end of autumn calving. When I arrived there were 14 cows left to give birth, and paddocks full of gorgeous calves.
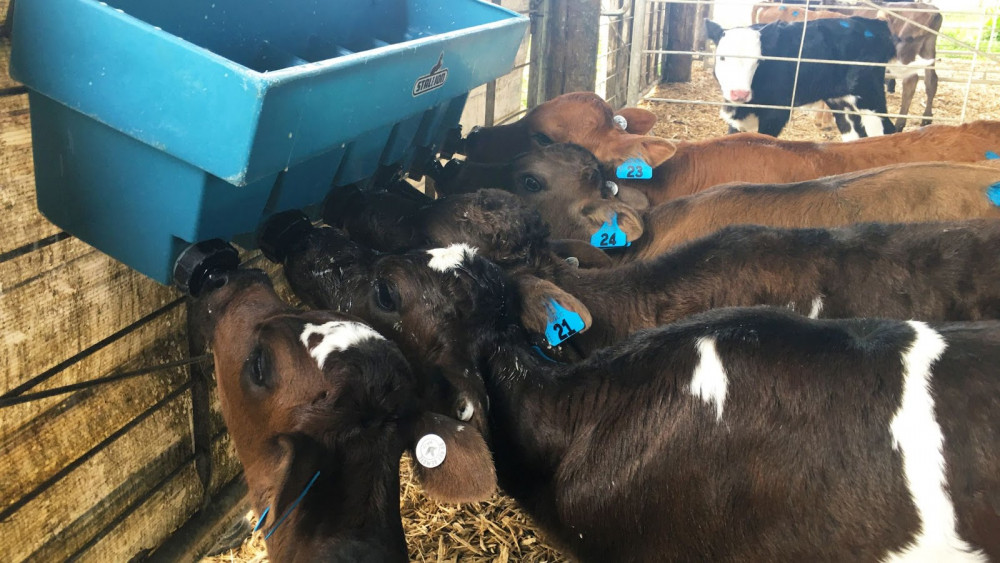

3-day-old-calves feeding
The most common practice for dairy calves in New Zealand is: about 30 percent of the female calves are kept and raised to become milking cows. Some farmers send their calves to be raised for beef - about 30 percent of beef raised in New Zealand comes from the dairy industry.
Otherwise, males and the rest of the females are sent to a meat processing plant around four days old.
Last year, the dairy industry had 4.9 million calves and nearly two million were killed within days or weeks of being born.
The biggest relief to me as a temporary employee at Mingiroa Farms was that Sam doesn’t send newborn calves to the slaughterhouse, instead having them raised to adulthood for beef. This meant I could enjoy the baby calves without fear of having to send them to a dog food factory.
Me trying to guide several-day-old calves onto the feeder teats. I keep calling them girls, forgetting that this pen was full of boys. I decided it was easier to just think of all the cows as girls that week.
Not only are they adorable, but they are also so funny. It was such a joy to see them get into this silly mood and bounce around the pens.
It’s also amazing how competent they are. Hours after being born they are walking and feeding themselves off their mothers. They are basically born at the equivalent of six-month-old humans, which is pretty amazing to watch.
A newly born calf standing for the first time
I could work on a dairy farm, but I couldn’t handle running one
At the end of my week, I asked myself: could I do this for a living?
It might be naive, but based on the cross section of work I had done that week, I really think I could.
There was an undeniable joy in how practical every day was, and how nice it was to be interacting with animals and the outdoors all the time.
What I couldn’t factor in was if I could sustain the lifestyle of the job long-term.
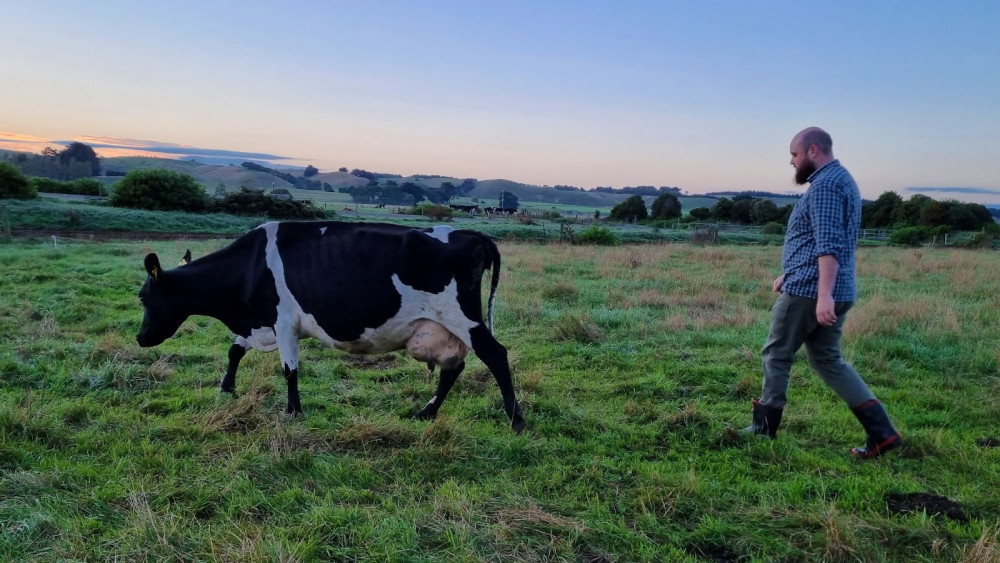

Me trying to get a cow moving along at 6am
And that was just in my capacity as an employee. Living with Sam that week I also got a taste of the reality of being the owner/operator. Every night, we had to go out again to check the farm before bed, as well as handling any emergencies that arose in the evening.
Before Sam took over the family farm, he had a conversation with an older dairy farmer who told him “it’s more a lifestyle than a job”. Sam had interpreted that to mean when you get into the groove, it’s a cruisey, go with the flow, kind of job.
Now, after running the farm for four years, he realised what the farmer actually meant is, “it’s more of a life, than a job”.
I realised that while I could happily be an employee on a dairy farm, I couldn’t handle being an owner/operator like Sam. To successfully run the farm, he has to be so many things - a biologist, chemist, vet, accountant, people and HR manager, labourer, cleaner, arborist, gardener, environment planner.
He has to deal with the responsibility and stress of keeping 300 animals happy and healthy, while also managing the farm’s finances, being a good manager to his staff, and not only maintaining the land, but trying to make it better.
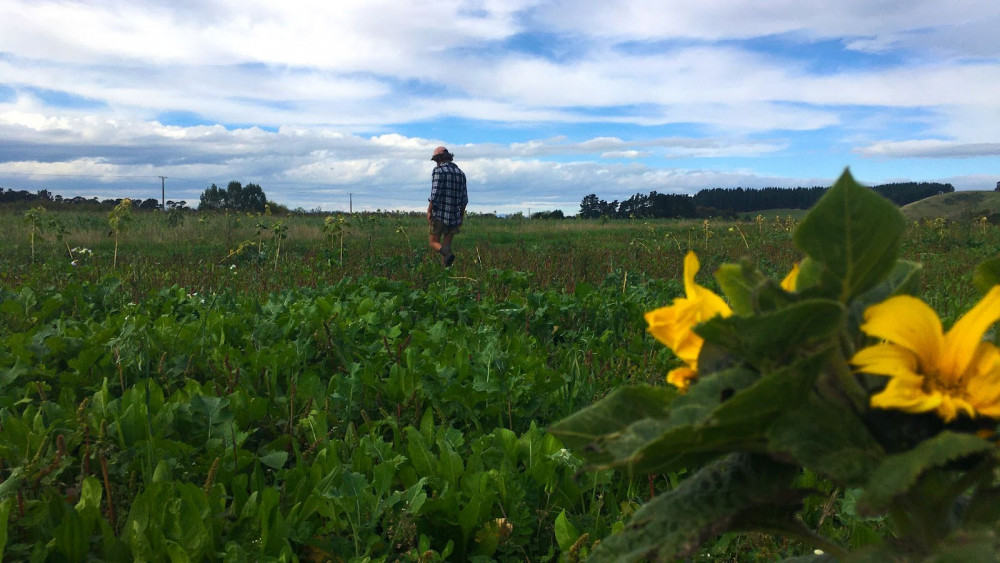 Sam checking a pasture
Sam checking a pastureI asked Sam, “If you could go back to the moment you decided to take over the farm, would you do it again?”
He said he’s not sure.
Even though Sam grew up on this farm - which has been in their family for nearly 170 years - it had been a sheep and beef farm up until 2008 when it was converted to dairy.
He didn’t actually plan to take over the farm, and had studied law at University.
But when he and his family saw the damage the intensive dairy approach was having on the land, they decided a new approach needed to be taken. Sam volunteered to take over the farm to try and find the most ethical and sustainable way to run it.
He hadn’t worked as a dairy farmer before, so the last four years have been a trial by fire as he worked to learn everything from scratch, while also trying to innovate.
“I certainly don’t regret anything,” he told me. “It has made me who I am and has tested what I stand for and has been incredibly rewarding.”
“At the same time, if I could go back I would do things a bit different, mainly around finding ways to ease the massive learning curve.”
Sustainable dairy needs sustainable thinkers
Sam is what we need our dairy farmers to be - passionate, caring, and dedicated to making dairy as ethical and environmentally sustainable as possible.
But dairy farming is struggling to get young people into the industry right now, which means fewer young innovative people like Sam.
The average age of dairy farmers is around 50 years old, and fewer young people are joining the industry. The lifestyle is not appealing and the environmental and ethical concerns about dairy have deterred some.
Even if young people did want to join the industry, skyrocketing property prices have restricted many from climbing the dairy ownership ladder.
If we want dairy in New Zealand to be sustainable, we need the best farmers possible. We essentially need a countryside full of Sams. But to do that, we need to make the industry more attractive. Some serious work needs to be done to find ways of making the it more ethically and environmentally sustainable, economically accessible and the lifestyle more appealing.
If we can do that, who knows, I might just make the switch myself.
Milk and Money is available to watch now on Re: and TVNZ OnDemand.
More stories: